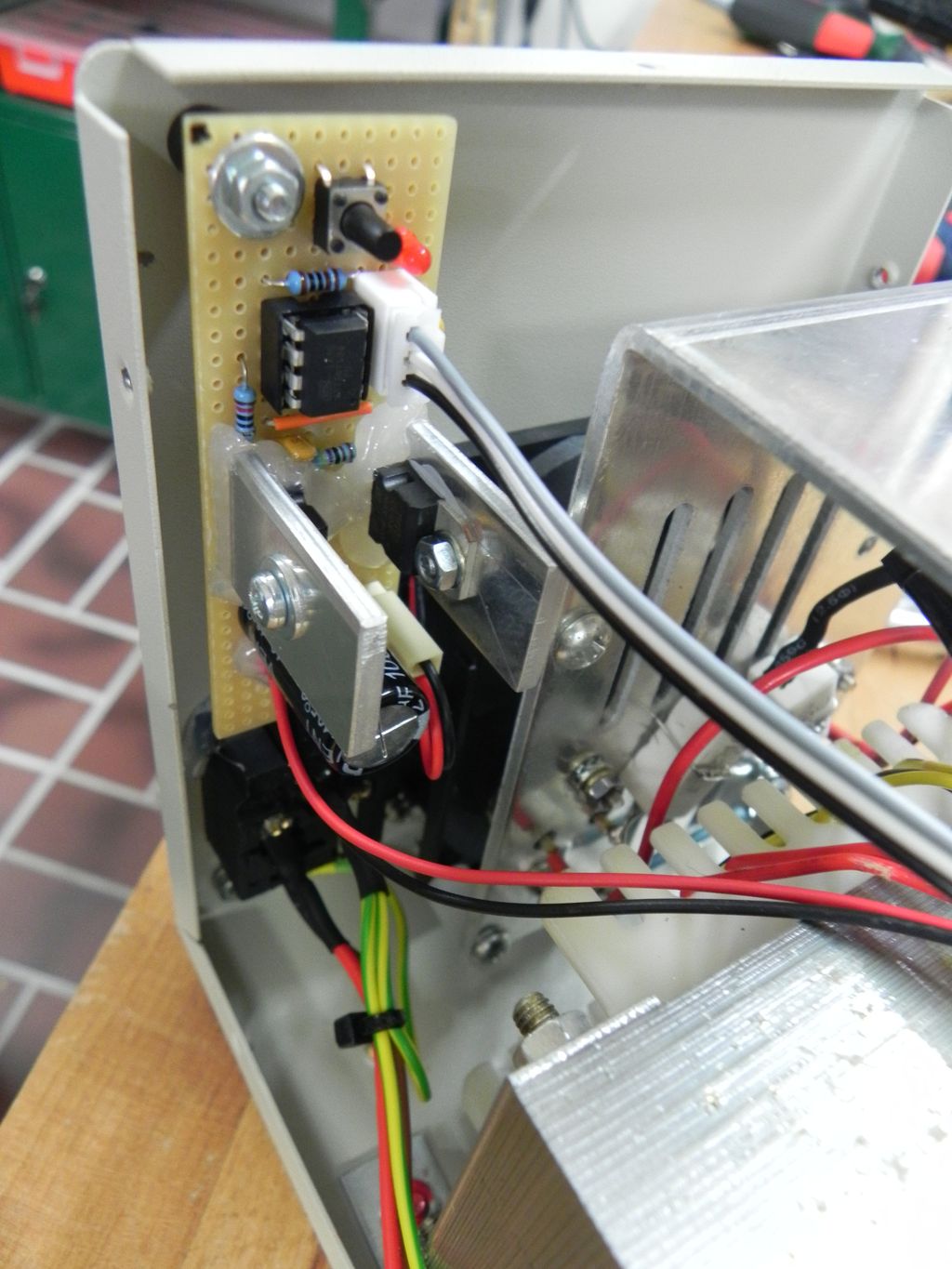
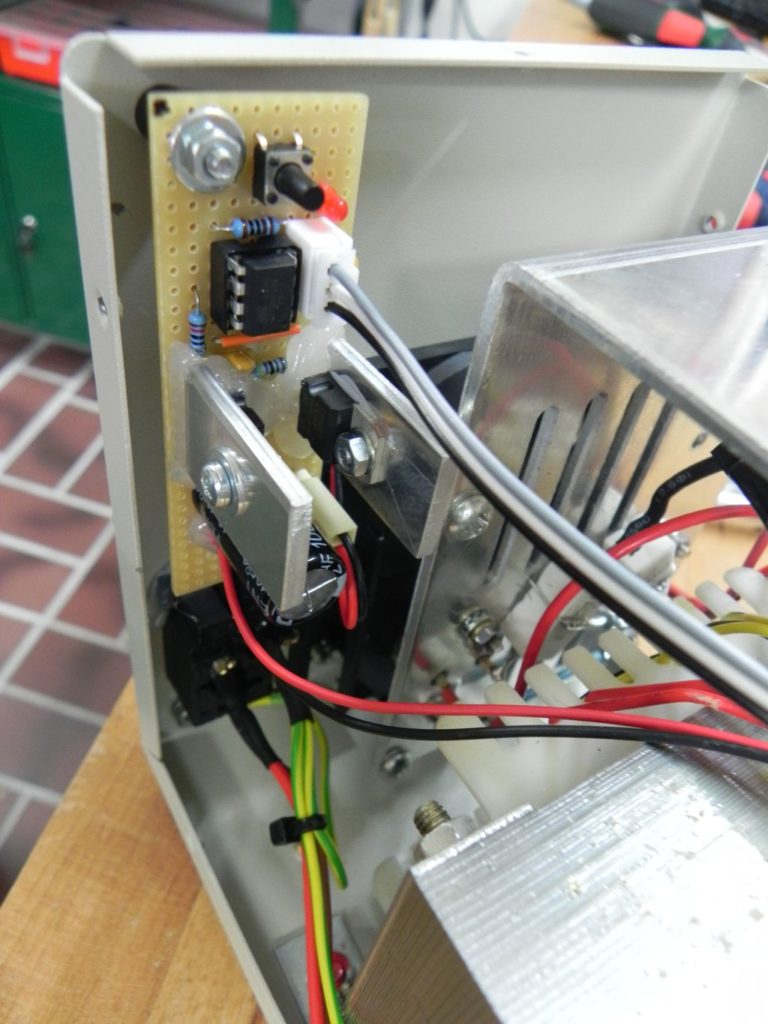
Like for the Lavolta power supply, I wanted to build a simple fan-controller circuit. Actually, I built this one first, and unlike the other one, which used the ATtiny85, I decided to build this one with a ATtiny13a. Because of this, the library for the DS18b20 digital sensor was too big to fit into the memory of the ATtiny13a. So I decided to use a TMP36 analog temperature sensor, since the controller already has a 10 Bit ADC and there is no need for another library.
This bench power supply actually came with a simple but working fan “controller”: The manufacturer ships these devices with a temperature switch, that turns the fan on, when it reaches a certain temperature (and off, if it drops below). There is nothing wrong with that! Still, I decided to go for the more complicated solution, since the switch can only turn the fan fully on or completely off, there is no in-between.

The basic setup is very simple: The micro-controller directly controls the base of a TIP120 Darlington transistor, which switches the 24 V power for the fan (using PWM). I know that a MOSFET would have been more efficient, but since the fan runs with 24 V, the voltage drop doesn’t matter that much. The LM7805 voltage regulator powers the micro-controller and the sensor (24 V to 5 V DC). Because the fan is a 24 V type, there was no need to use a buck converter or linear regulator.
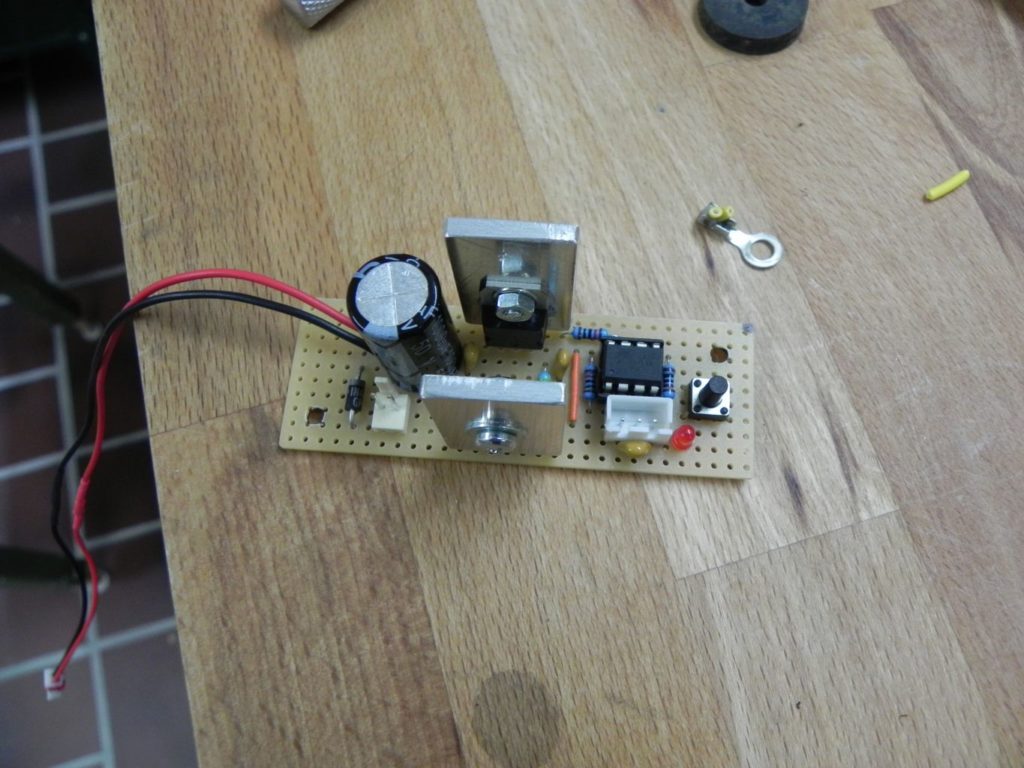
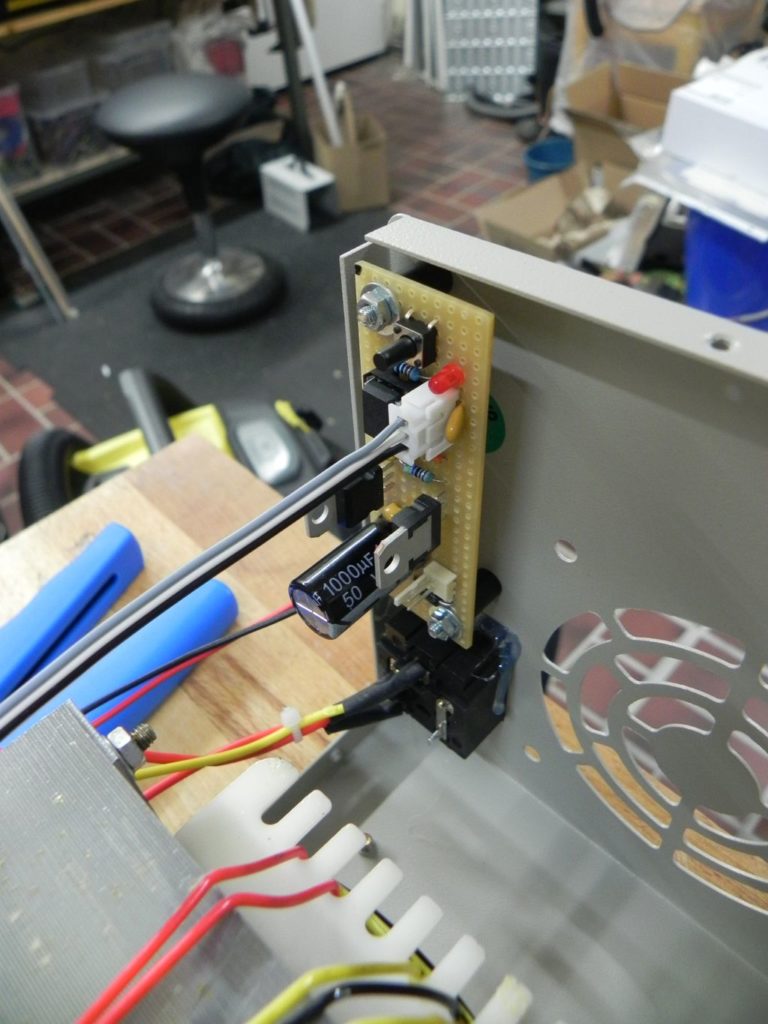




Below you’ll find the source code written using avr-libc and avr-gcc for compiling it.
#ifndef __AVR_ATtiny13A__
#define __AVR_ATtiny13A__
#endif
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#define P_LED PB0
#define PORT_LED PORTB0
#define DD_LED DDB0
#define P_FANPWM PB1
#define DD_FANPWM DDB1
#define P_BUTTON PB2
#define PORT_BUTTON PORTB2
#define PIN_BUTTON PINB2
#define P_TMP36 PB4
#define ADC_TMP36 ADC2
/*
* Pin 1 - Reset
* Pin 2 - N/A
* Pin 3 - [ADC2] TMP36 Sensor
* Pin 4 - GND
* Pin 5 - [PB0] LED
* Pin 6 - [OC0B] PWM Lüfter
* Pin 7 - [PB2] Taster
* Pin 8 - VCC
*/
const uint8_t PWM_BOTTOM = 0;
const uint8_t PWM_TOP = 47; // 48 Werte/Stufen (0-47)
const uint8_t FAN_MINIMUM = 10; // Achtung: Lüfter läuft erst bei 7 an!
const int8_t TEMPERATURE_OFFSET = 0; // Ausgleichwert für Temperatur
const uint8_t VREF = 5;
uint16_t volatile to_counter; // Zähler für Timer-Overflows
uint8_t seconds_counter;
uint16_t volatile adc_raw; // Letzer gemessener ADC-Wert
int8_t temperature_1s_ago;
int8_t temperature_1m_ago;
// Timer Overflow Interrupt ISR
// Aufruf der ISR setzt das TOV0 Flag im TIFR Register zurück.
ISR(TIM0_OVF_vect) {
to_counter++;
}
// ADC Conversion Complete Interrupt ISR
// Aufruf der ISR setzt das ADIF Flag im ADCSRA Register zurück.
ISR(ADC_vect) {
adc_raw = ADC;
// Nächste Messung startet automatisch (Free Running Mode)
}
void setupTimer0(void) {
// Register TCCR0A/B initialisieren
// Fast-PWM Modus wählen (TOP = OCR0A)
// OCR0B entspricht Duty-Cycle
TCCR0A |= (1 << COM0B1) | (0 << COM0B0) | (1 << WGM01) | (1 << WGM00);
// Counter initialisieren bzw. festlegen
OCR0A = PWM_TOP;
OCR0B = PWM_BOTTOM; // Duty-Cycle
// Prescaler auf 8 setzen
// Formel für Fast-PWM-Frequenz: F_CPU / (Prescaler * 256)
// 9,6 MHz: 9.600.000 / (8 * 48) = 25.000 Hz --> 25 kHz
TCCR0B |= (1 << WGM02) | (0 << CS02) | (1 << CS01) | (0 << CS00);
// Timer Overflow Interrupt einschalten
// Erhöht Zählervariable
TIMSK0 |= (1 << TOIE0);
}
void setupADC(void) {
// ADC Multiplexer Selection Register
// REFS0: VCC als Referenzspannung (Standard).
// ADLAR: Left adjust ausschalten (siehe unten!)
// MUX[1:0]: ADC2 (PB4, Pin 3) als analogen Eingang festlegen.
ADMUX |= (0 << REFS0) | (0 << ADLAR) | (1 << MUX1) | (0 << MUX0);
// Digitalen Input für analogen Pin abschalten
DIDR0 |= (1 << ADC2D);
// ADC Control and Status Register A
// ADEN: ADC einschalten
// ADSC: Einzelne Messung starten
// ADIE: ADC Conversion Complete Interrupt einschalten
// ADPS[2:0]: ADC Prescaler auf 64 (Ziel: zwischen 50 und 200 kHz)
// 9,6 MHz: 9.600.000 Hz / 64 = 150.000 Hz --> 150 kHz
ADCSRA |= (1 << ADEN) | (1 << ADSC) | (1 << ADIE) | (1 << ADPS2) | (1 << ADPS1) | (0 << ADPS0);
// Ergebnis wird in ADCL und ADCH (ADC Low Byte und ADC High Byte)
// gespeichert, da 10 Bit Wert. ADC enthält vollständigen Wert.
while (ADCSRA & (1 << ADSC)); // Ergebnis abwarten...
(void) (ADC); // Erste Messung verwerfen (lt. Datenblatt empfohlen)
}
int8_t calculateTemperature(uint16_t adc_value) {
// TMP36 Sensor: 10 mV entsprechen 1 °C (linearer)
// Gemessener Wert wird zunächst auf die 5 V Referenz bezogen,
// danach 0,5 V abgezogen, geteilt und das Ergebnis ganzzahlig gerunded.
uint16_t voltage = ((uint32_t) adc_value) * VREF * 1000 / 1024;
voltage -= 500; // TMP36 Voltage Offset abziehen
int8_t temperature = (voltage + 5) / 10;
temperature += TEMPERATURE_OFFSET;
return temperature;
}
void delayTOs(uint16_t overflows) {
uint8_t sreg_before = SREG; // Interrupt Status (ein/aus) speichern
cli();
uint16_t to_counter_before = to_counter; // Zählerstand speichern
to_counter = 0;
sei();
while (to_counter < overflows) {} // Warten...
cli();
to_counter = to_counter_before; // Zählerstand wiederherstellen
SREG = sreg_before; // Interrupts auf alten Zustand setzen
}
int main(void) {
DDRB |= (1 << DD_FANPWM) | (1 << DD_LED);
PORTB |= (1 << PORTB3); // Unbenutzen Pin 2 Pull-up einschalten
//PORTB |= (1 << PORT_BUTTON); // Taster Pull-up ein (externer Pullup 10k)
setupADC();
setupTimer0(); // PWM, Timer-Overflow-Counter
// Einmalige Messung zur Initialisierung der globalen Temperaturvariablen
ADCSRA |= (1 << ADSC);
while (ADCSRA & (1 << ADSC)); // Ergebnis abwarten...
temperature_1s_ago = calculateTemperature(ADC);
temperature_1m_ago = temperature_1s_ago;
// ADC in Free Running Mode versetzen und erste Messung starten
ADCSRA |= (1 << ADSC) | (1 << ADATE);
to_counter = 0;
seconds_counter = 0;
sei(); // Interrupts einschalten
while (1) {
// Wenn eine Sekunde vergangen ist... (Regelung)
if (to_counter > ((uint16_t) 25 * 1000)) {
cli();
PORTB ^= (1 << PORT_LED); // LED umschalten (Aktivitätsanzeige)
int8_t temperature = calculateTemperature(adc_raw); // ADC-Wert verarbeiten
// Berechnung des Temperaturwerts für PWM mit Gewichtung
int16_t tv = temperature_1m_ago * 15;
tv += temperature_1s_ago * 4;
tv += temperature;
tv = (tv + 5) / 20;
// Achtung: Lüfter läuft erst bei einem PWM Duty-Cycle von 7 an!
if (tv <= 23) {
OCR0B = PWM_BOTTOM; // Lüfter aus
} else if (tv == 24) {
OCR0B = FAN_MINIMUM; // Minimale Drehzahl des Lüfters
} else if (tv == 25) {
OCR0B = 12;
} else if (tv == 26) {
OCR0B = 15;
} else if (tv == 27) {
OCR0B = 19;
} else if (tv == 28) {
OCR0B = 23;
} else if (tv == 29) {
OCR0B = 27;
} else if (tv == 30) {
OCR0B = 30;
} else if (tv == 31) {
OCR0B = 33;
} else if (tv == 34) {
OCR0B = 36;
} else if (tv == 37) {
OCR0B = 39;
} else if (tv == 40) {
OCR0B = 42;
} else if (tv == 43) {
OCR0B = 45;
} else {
OCR0B = PWM_TOP;
}
// Sicherstellen, dass der ADC läuft
if (!(ADCSRA & (1 << ADSC))) {
ADCSRA |= (1 << ADSC) | (1 << ADATE);
}
// Wenn eine Minute vergangen ist...
if (++seconds_counter >= 60) {
seconds_counter = 0;
temperature_1m_ago = temperature;
}
temperature_1s_ago = temperature;
to_counter = 0;
sei();
}
// Wenn der Taster gedrückt wird... (Testlauf starten)
if (!(PINB & (1 << PIN_BUTTON))) {
cli();
PORTB |= (1 << PORT_LED); // LED ein
OCR0B = PWM_BOTTOM;
delayTOs((uint16_t) 50 * 1000);
for (uint8_t i = PWM_BOTTOM; i < PWM_TOP; i++) { // Hochdrehen
OCR0B = i;
delayTOs(5000);
}
OCR0B = PWM_TOP;
delayTOs((uint16_t) 50 * 1000);
for (uint8_t i = PWM_TOP; i > PWM_BOTTOM; i--) { // Runterdrehen
OCR0B = i;
delayTOs(5000);
}
PORTB &= ~(1 << PORT_LED); // LED aus
sei();
}
}
}